Deep vein thrombosis popular science series one
Release time:
2022-05-20
Source:
Deep vein thrombosis popular science series one
Deep vein thrombosis popular science series one
What is an invisible killer?
Name: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Occupation: The world's three major vascular killers
Appearance: Blood clots formed in human veins
Hound: more common in the legs and lungs
God assists: slow blood flow, blood hypercoagulable state, vascular intimal injury
Two of his men:
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) formation: predisposition to PE, post-thrombotic syndrome
Pulmonary embolism (PE): particularly dangerous and life-threatening
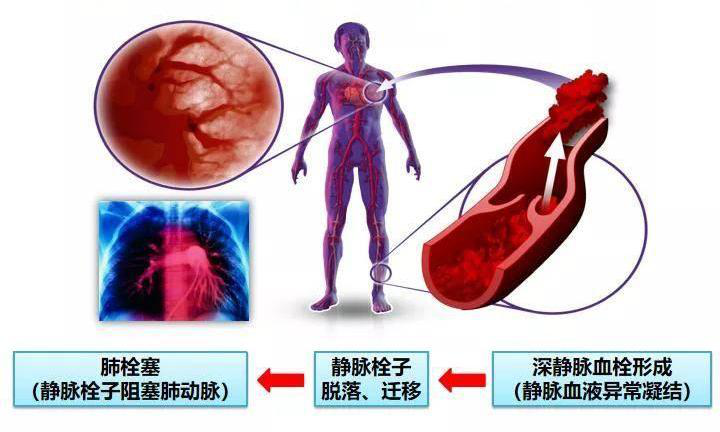
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is recognized as a common "killer" of patients, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) formation and pulmonary embolism (PE). However, because 80% of deep vein thrombosis has no clinical manifestations and 70% of pulmonary embolism is found after death, it is also called "silent killer".
Is deep vein thrombosis really that scary?
Of course! Experts said that deep vein thrombosis has the characteristics of "three highs and one low", high risk of occurrence, high mortality, high missed diagnosis rate, and low detection rate.
High risk of occurrence
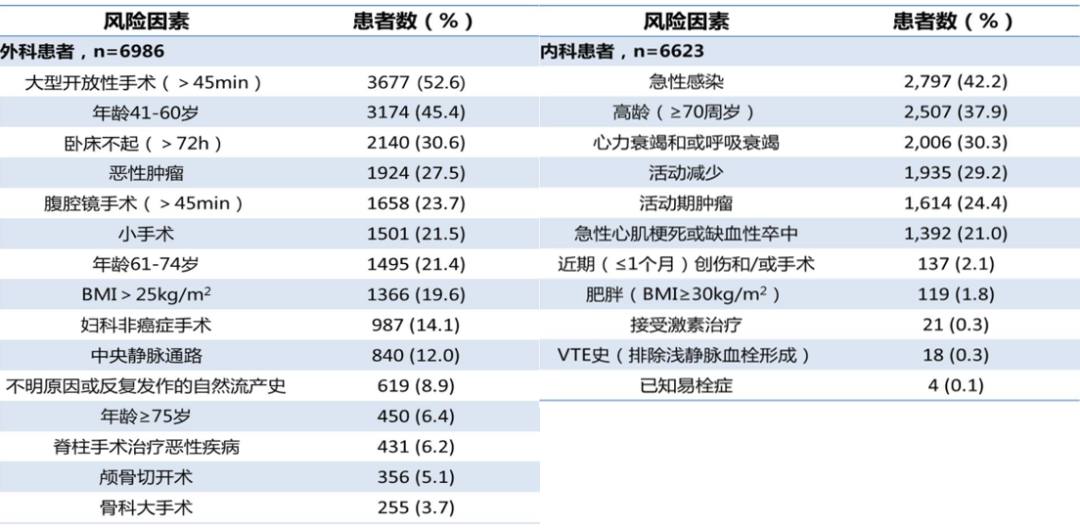
In January 2019, the team of professors Wang Chen and Zhai Zhenguo published "Risk Characteristics and Prevention of VTE in Internal Medicine and Surgery Hospitalized Patients, Determination of Risk Characteristics of Venous Thromboembolism in Chinese Hospitalized Patients (DissolVE-2)" in the international authoritative magazine CHEST. The results show that 36.6 of Chinese internal medicine hospitalized patients are high-risk groups for VTE. 32.7 of surgical inpatients are at medium risk and 53.4 are at high risk.
high mortality rate
The mortality and disability rates of pulmonary embolism are high. Recent international registration studies have shown that the 7-day all-cause mortality rate of pulmonary embolism is 1.9-2.9, and the 30-day all-cause mortality rate is 4.9-6.6.
high rate of missed diagnosis
Deep vein thrombosis is often hidden, the incidence is hidden, and when it develops into a serious state such as pulmonary embolism, it is not as "daring" as the embolus of myocardial infarction, and it is easy to be found by doctors. Some people's early symptoms are very hidden. They often go to see a doctor first because of syncope, cough, dyspnea, chest pain, hemoptysis and other manifestations. These symptoms will lead doctors to find the cause of heart disease and pulmonary infectious diseases first. It confuses the public and paralyzes the doctor, so it is often at large.
The culprit of deep vein thrombosis?
The classic triangle theory of deep vein thrombosis holds that:
slow blood flow
hypercoagulable state of blood
vascular intimal injury
As long as one of these three elements exists, it can lead to the formation of blood clots.
Such as age, blood viscosity increased, blood pressure increased, blood lipids increased, these people are prone to deep vein thrombosis. The most common trigger is braking. We know that the blood of the lower limbs is to be contracted back to the heart through the calf muscle pump. If it is braked, the calf muscle pump cannot be contracted, and the blood reflux is difficult, leading to thrombosis.
The cause of immobilization is mostly post-operative, especially orthopedic surgery. Orthopedic patients often need to stay in bed after surgery to stop movement. Joint replacement surgery, such as knee replacement, hip replacement surgery after the occurrence of deep vein thrombosis is very high, about 40%-80%. Other surgical procedures, postoperative DVT also occurs in 20%-40%.
Deep vein thrombosis is 6 to 10 times more common in pregnant women than in non-pregnant women. In addition, cancer patients are prone to deep vein thrombosis, and about 20-30% of cancer patients will develop deep vein thrombosis.
DVT is also prone to long-distance flights. Trapped in a small space and inactive for a long time, slow blood flow is prone to occur. This is also our common "economy class syndrome". Deaths caused by VTE already account for the second leading cause of death in long-distance travel.
Evaluation of deep vein thrombosis
In clinical work, in order to simply and accurately screen out the VTE risk population, the Caprini assessment scale and Padua assessment scale are generally used to identify patients who may have deep vein thrombosis, and early intervention and preventive measures are applied.
Caprini assessment scale: contains about 40 different risk factors for thrombosis, basically covering all risk factors for VTE in surgical and hospitalized patients, and VTE risk scores are scored by these risk factors. Patients with a score of moderate to higher risk require physical combination medication to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
Padua assessment scale: a commonly used VTE risk grading assessment model for non-surgical patients, which classifies the risk of VTE in patients according to the total score. Patients with a high-risk score require a physical combination of medications to prevent deep vein thrombosis.

Early prevention of deep vein thrombosis
Basic prevention
Drink plenty of water, and quit smoking, alcohol, good control of blood sugar, blood lipids;
Change your position regularly during bed rest, you can try to do ankle flexion and expansion exercise, knee telescopic exercise, etc;
Avoid hard pillows and excessive hip flexion under the knee. When the condition allows, the affected limb can be elevated to promote venous return.
Physical prevention
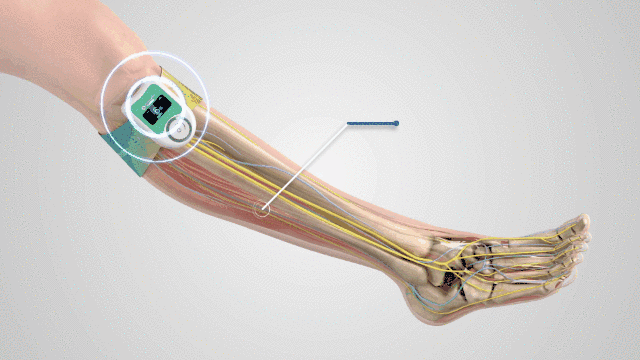
Physical prevention is one of the important measures to prevent deep venous thrombosis of lower extremities. Neuromuscular electrical stimulator, intermittent pneumatic compression device and venous plantar pump can be used according to the doctor's advice.
Dewefor®The neuromuscular electrical stimulator stimulates the common peroneal nerve through neuromuscular electrical stimulation technology (NMES), so that the calf and plantar muscles produce rhythmic contraction and relaxation activities, simulating the physiological state of human body during normal activities, forming a "muscle pump" effect, effectively squeezing the lower limb blood vessels, strengthening the pumping efficiency, improving the blood flow velocity of lower limb veins, arteries and microcirculation, and promoting lymphatic reflux, to prevent deep vein thrombosis, regression edema, promote wound healing.
The guidelines suggest that compared with anticoagulant drugs, physical prevention of bleeding risk is less, so for people with bleeding risk factors, physical prevention of deep vein thrombosis can be used first, and then combined with drugs for prevention after the bleeding risk is relieved.
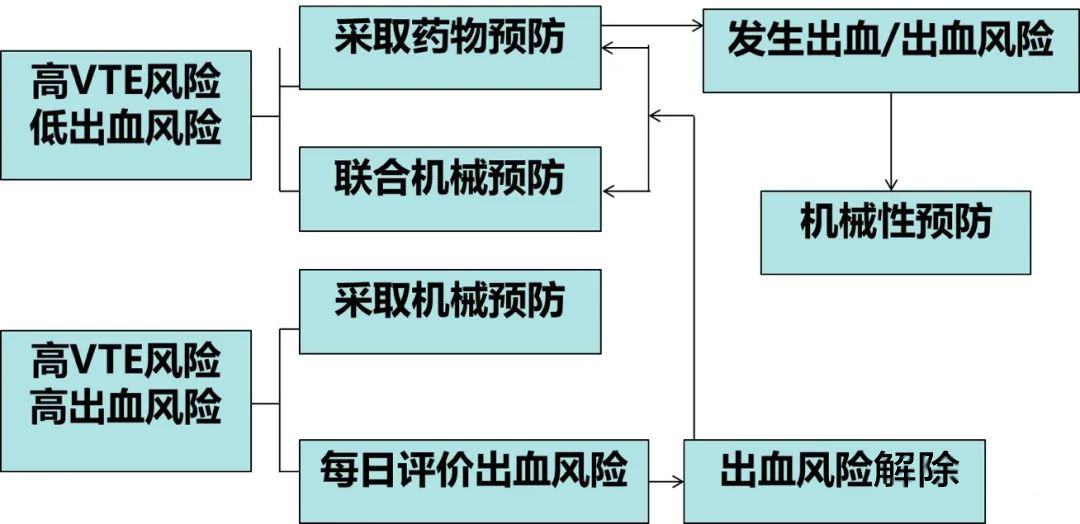
drug prevention
If necessary, anticoagulant drugs can be applied according to the doctor's advice to prevent the formation of thrombosis. Commonly used preventive drugs include unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, rivaroxaban and so on.
Related News


